Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Bolt pretension#
This example demonstrates how to insert a Static Structural analysis into a new Mechanical session and execute a sequence of Python scripting commands that define and solve a bolt-pretension analysis. Scripts then evaluate the following results: deformation, equivalent stresses, contact, and bolt.
Import the necessary libraries#
from pathlib import Path
import typing
from PIL import Image
from ansys.mechanical.core import App
from ansys.mechanical.core.examples import delete_downloads, download_file
from matplotlib import image as mpimg
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
Initialize the embedded application#
app = App()
print(app)
# Import the enums and global variables instead of using app.update_globals(globals())
# or App(globals=globals())
from ansys.mechanical.core.embedding.enum_importer import *
from ansys.mechanical.core.embedding.global_importer import Quantity
from ansys.mechanical.core.embedding.transaction import Transaction
Ansys Mechanical [Ansys Mechanical Enterprise]
Product Version:252
Software build date: 06/13/2025 11:25:56
Configure graphics for image export#
# Set camera orientation
graphics = app.Graphics
camera = graphics.Camera
camera.SetSpecificViewOrientation(ViewOrientationType.Iso)
camera.SetFit()
camera.Rotate(180, CameraAxisType.ScreenY)
# Set camera settings for 720p resolution
graphics_image_export_settings = Ansys.Mechanical.Graphics.GraphicsImageExportSettings()
graphics_image_export_settings.Resolution = GraphicsResolutionType.EnhancedResolution
graphics_image_export_settings.Background = GraphicsBackgroundType.White
graphics_image_export_settings.CurrentGraphicsDisplay = False
graphics_image_export_settings.Width = 1280
graphics_image_export_settings.Height = 720
Set the geometry import group for the model#
# Set the model
model = app.Model
# Create a geometry import group for the model
geometry_import_group = model.GeometryImportGroup
# Add the geometry import to the group
geometry_import = geometry_import_group.AddGeometryImport()
# Set the geometry import format
geometry_import_format = (
Ansys.Mechanical.DataModel.Enums.GeometryImportPreference.Format.Automatic
)
# Set the geometry import preferences
geometry_import_preferences = Ansys.ACT.Mechanical.Utilities.GeometryImportPreferences()
geometry_import_preferences.ProcessNamedSelections = True
Download and import the geometry#
# Download the geometry file from the ansys/example-data repository
geometry_path = download_file(
"example_06_bolt_pret_geom.agdb", "pymechanical", "00_basic"
)
# Import/reload the geometry from the CAD (.agdb) file using the provided preferences
geometry_import.Import(
geometry_path, geometry_import_format, geometry_import_preferences
)
# Visualize the model in 3D
app.plot()
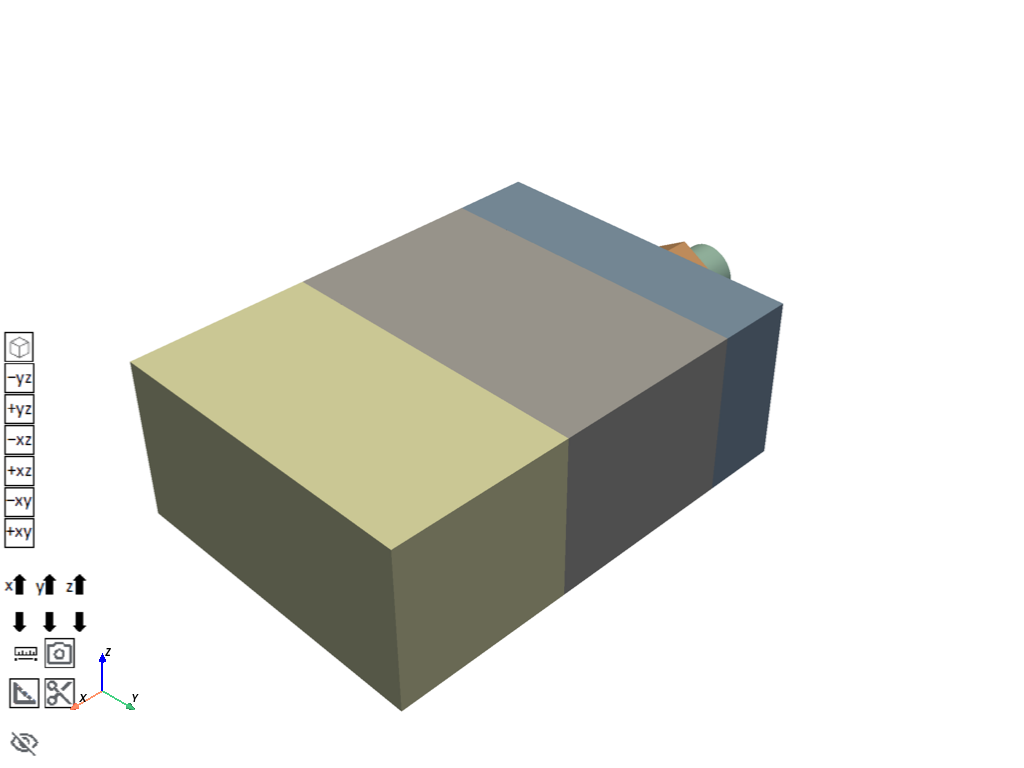
Download and import the materials#
Download the material files from the ansys/example-data repository
copper_material_file_path = download_file(
"example_06_Mat_Copper.xml", "pymechanical", "00_basic"
)
steel_material_file_path = download_file(
"example_06_Mat_Steel.xml", "pymechanical", "00_basic"
)
Add materials to the model and import the material files
model_materials = model.Materials
model_materials.Import(copper_material_file_path)
model_materials.Import(steel_material_file_path)
Define analysis and unit system#
Add static structural analysis to the model
model.AddStaticStructuralAnalysis()
static_structural = model.Analyses[0]
static_structural_solution = static_structural.Solution
static_structural_analysis_setting = static_structural.Children[0]
Store the named selections
named_selections_dictionary = {}
named_selections_list = [
"block3_block2_cont",
"block3_block2_targ",
"shank_block3_cont",
"shank_block3_targ",
"block1_washer_cont",
"block1_washer_targ",
"washer_bolt_cont",
"washer_bolt_targ",
"shank_bolt_targ",
"shank_bolt_cont",
"block2_block1_cont",
"block2_block1_targ",
]
Set the unit system to Standard NMM
app.ExtAPI.Application.ActiveUnitSystem = MechanicalUnitSystem.StandardNMM
Get tree objects for each named selection
for named_selection in named_selections_list:
named_selections_dictionary[named_selection] = app.DataModel.GetObjectsByName(
named_selection
)[0]
Create a list with material assignment for each model.Geometry.Children index
children_materials = ["Steel", "Copper", "Copper", "Steel", "Steel", "Steel"]
Assign surface materials to the model.Geometry bodies
geometry = model.Geometry
for children_index, material_name in enumerate(children_materials):
# Get the surface of the body
surface = geometry.Children[children_index].Children[0]
# Assign the material to the surface
surface.Material = material_name
Add and define a coordinate system#
Add a coordinate system to the model
coordinate_systems = model.CoordinateSystems
coordinate_system = coordinate_systems.AddCoordinateSystem()
Define the coordinate system and set its axis properties
coordinate_system.OriginDefineBy = CoordinateSystemAlignmentType.Fixed
coordinate_system.OriginX = Quantity(-195, "mm")
coordinate_system.OriginY = Quantity(100, "mm")
coordinate_system.OriginZ = Quantity(50, "mm")
coordinate_system.PrimaryAxis = CoordinateSystemAxisType.PositiveZAxis
Create functions for contact region set up#
Add a contact region to the body with the specified source location, target location, and contact type
def set_contact_region_locations_and_types(
body: typing.Union[
Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections,
Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections.ConnectionGroup,
],
source_location: Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.NamedSelection,
target_location: Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.NamedSelection,
contact_type: ContactType,
) -> Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections.ContactRegion:
"""Add a contact region to the body with the specified source location, target location,
and contact type.
Parameters
----------
body : Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections or
Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections.ConnectionGroup
The body to which the contact region will be added.
source_location : Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.NamedSelection
The source location for the contact region.
target_location : Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.NamedSelection
The target location for the contact region.
contact_type : ContactType
The type of contact for the contact region.
Returns
-------
Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections.ContactRegion
The created contact region.
"""
contact_region = body.AddContactRegion()
contact_region.SourceLocation = source_location
contact_region.TargetLocation = target_location
contact_region.ContactType = contact_type
return contact_region
Set the friction coefficient, small sliding, and update stiffness settings for the contact region
def advanced_contact_settings(
contact_region: Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections.ContactRegion,
friction_coefficient: int,
small_sliding: ContactSmallSlidingType,
update_stiffness: UpdateContactStiffness,
) -> None:
"""Set the friction coefficient, small sliding, and update stiffness settings for the
contact region.
Parameters
----------
contact_region : Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections.ContactRegion
The contact region to set the settings for.
friction_coefficient : int
The friction coefficient for the contact region.
small_sliding : ContactSmallSlidingType
The small sliding setting for the contact region.
update_stiffness : UpdateContactStiffness
The update stiffness setting for the contact region.
"""
contact_region.FrictionCoefficient = friction_coefficient
contact_region.SmallSliding = small_sliding
contact_region.UpdateStiffness = update_stiffness
Add a command snippet to the contact region with the specified Archard Wear Model
def add_command_snippet(
contact_region: Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections.ContactRegion,
archard_wear_model: str,
) -> None:
"""Add a command snippet to the contact region with the specified Archard Wear Model.
Parameters
----------
contact_region : Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Connections.ContactRegion
The contact region to add the command snippet to.
archard_wear_model : str
The Archard Wear Model command snippet to add to the contact region.
"""
contact_region_cmd = contact_region.AddCommandSnippet()
contact_region_cmd.AppendText(archard_wear_model)
Add and define contact regions#
Set up the model connections and delete the existing connections for ConnectionGroups
connections = model.Connections
for connection in connections.Children:
if connection.DataModelObjectCategory == DataModelObjectCategory.ConnectionGroup:
app.DataModel.Remove(connection)
Set the archard wear model and get the named selections from the model
# Set the archard wear model
archard_wear_model = """keyopt,cid,9,5
rmodif,cid,10,0.00
rmodif,cid,23,0.001"""
# Get named selections from the model for contact regions
named_selections = model.NamedSelections
Add a contact region for the model’s named selections Children 0 and 1 with the specified contact type
contact_region = set_contact_region_locations_and_types(
body=connections,
source_location=named_selections.Children[0],
target_location=named_selections.Children[1],
contact_type=ContactType.Frictional,
)
# Set the friction coefficient, small sliding, and update stiffness settings for the contact region
advanced_contact_settings(
contact_region=contact_region,
friction_coefficient=0.2,
small_sliding=ContactSmallSlidingType.Off,
update_stiffness=UpdateContactStiffness.Never,
)
# Add a command snippet to the contact region with the specified Archard Wear Model
add_command_snippet(contact_region, archard_wear_model)
Set the connection group for the contact regions
connection_group = connections.Children[0]
Add a contact region for the model’s named selections Children 2 and 3 with the specified contact type
contact_region_2 = set_contact_region_locations_and_types(
body=connection_group,
source_location=named_selections.Children[3],
target_location=named_selections.Children[2],
contact_type=ContactType.Bonded,
)
contact_region_2.ContactFormulation = ContactFormulation.MPC
Add a contact region for the model’s named selections Children 4 and 5 with the specified contact type
contact_region_3 = set_contact_region_locations_and_types(
body=connection_group,
source_location=named_selections.Children[4],
target_location=named_selections.Children[5],
contact_type=ContactType.Frictional,
)
# Set the friction coefficient, small sliding, and update stiffness settings for the contact region
advanced_contact_settings(
contact_region=contact_region_3,
friction_coefficient=0.2,
small_sliding=ContactSmallSlidingType.Off,
update_stiffness=UpdateContactStiffness.Never,
)
# Add a command snippet to the contact region with the specified Archard Wear Model
add_command_snippet(contact_region_3, archard_wear_model)
Add a contact region for the model’s named selections Children 6 and 7 with the specified contact type
contact_region_4 = set_contact_region_locations_and_types(
body=connection_group,
source_location=named_selections.Children[6],
target_location=named_selections.Children[7],
contact_type=ContactType.Bonded,
)
contact_region_4.ContactFormulation = ContactFormulation.MPC
Add a contact region for the model’s named selections Children 8 and 9 with the specified contact type
contact_region_5 = set_contact_region_locations_and_types(
body=connection_group,
source_location=named_selections.Children[9],
target_location=named_selections.Children[8],
contact_type=ContactType.Bonded,
)
contact_region_5.ContactFormulation = ContactFormulation.MPC
Add a contact region for the model’s named selections Children 10 and 11 with the specified contact type
contact_region_6 = set_contact_region_locations_and_types(
body=connection_group,
source_location=named_selections.Children[10],
target_location=named_selections.Children[11],
contact_type=ContactType.Frictional,
)
# Set the friction coefficient, small sliding, and update stiffness settings for the contact region
advanced_contact_settings(
contact_region=contact_region_6,
friction_coefficient=0.2,
small_sliding=ContactSmallSlidingType.Off,
update_stiffness=UpdateContactStiffness.Never,
)
# Add a command snippet to the contact region with the specified Archard Wear Model
add_command_snippet(contact_region_6, archard_wear_model)
Create functions to set up the mesh#
Set the mesh method location for the specified method and object name
def set_mesh_method_location(method, object_name: str, location_type: str = "") -> None:
"""Set the location of the method based on the specified name and location type.
Parameters
----------
method : Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.MeshMethod
The method to set the location for.
object_name : str
The name of the object to set the location for.
location_type : str, optional
The type of location to set for the method. Can be "source", "target", or empty string.
Default is an empty string.
"""
# Get the tree object for the specified name
tree_obj = app.DataModel.GetObjectsByName(object_name)[0]
# Set the method location based on the specified location type
if location_type == "source":
method.SourceLocation = tree_obj
elif location_type == "target":
method.TargetLocation = tree_obj
else:
method.Location = tree_obj
Add a mesh sizing to the mesh with the specified name, quantity value, and measurement
def add_mesh_sizing(mesh, object_name: str, element_size: Quantity) -> None:
"""Add a mesh sizing to the mesh with the specified name, quantity value, and measurement.
Parameters
----------
mesh : Ansys.ACT.Automation.Mechanical.Mesh
The mesh to add the sizing to.
object_name : str
The name of the object to set the sizing for.
element_size : Quantity
The element size for the mesh sizing.
"""
# Add sizing to the mesh
body_sizing = mesh.AddSizing()
# Get the tree object for the specified name
body_sizing.Location = app.DataModel.GetObjectsByName(object_name)[0]
# Set the element size to the mesh
body_sizing.ElementSize = element_size
Add mesh methods, sizing, and face meshing#
Add the mesh sizing to the bodies_5 and shank objects
mesh = model.Mesh
add_mesh_sizing(mesh=mesh, object_name="bodies_5", element_size=Quantity(15, "mm"))
add_mesh_sizing(mesh=mesh, object_name="shank", element_size=Quantity(7, "mm"))
Add an automatic method to the mesh and set the method type
hex_method = mesh.AddAutomaticMethod()
hex_method.Method = MethodType.Automatic
# Set the method location for the all_bodies object
set_mesh_method_location(method=hex_method, object_name="all_bodies")
Add face meshing to the mesh and set the MappedMesh property to False
face_meshing = mesh.AddFaceMeshing()
face_meshing.MappedMesh = False
# Set the method location for the face meshing
set_mesh_method_location(method=face_meshing, object_name="shank_face")
Add an automatic method to the mesh, set the method type, and set the source target selection
sweep_method = mesh.AddAutomaticMethod()
sweep_method.Method = MethodType.Sweep
sweep_method.SourceTargetSelection = 2
# Set the method locations for the shank, shank_face, and shank_face2 objects
set_mesh_method_location(method=sweep_method, object_name="shank")
set_mesh_method_location(
method=sweep_method, object_name="shank_face", location_type="source"
)
set_mesh_method_location(
method=sweep_method, object_name="shank_face2", location_type="target"
)
Activate and generate the mesh
mesh.Activate()
mesh.GenerateMesh()
# Fit the view to the entire model
camera.SetFit()
# Set the path for the output files (images, gifs, mechdat)
output_path = Path.cwd() / "out"
mesh_image_path = str(output_path / "mesh.png")
# Set the image export format and export the image
image_export_format = GraphicsImageExportFormat.PNG
graphics.ExportImage(
mesh_image_path, image_export_format, graphics_image_export_settings
)
Create a function to display the image using matplotlib
def display_image(
image_path: str,
pyplot_figsize_coordinates: tuple = (16, 9),
plot_xticks: list = [],
plot_yticks: list = [],
plot_axis: str = "off",
):
"""Display the image with the specified parameters."""
# Set the figure size based on the coordinates specified
plt.figure(figsize=pyplot_figsize_coordinates)
# Read the image from the file into an array
plt.imshow(mpimg.imread(image_path))
# Get or set the current tick locations and labels of the x-axis
plt.xticks(plot_xticks)
# Get or set the current tick locations and labels of the y-axis
plt.yticks(plot_yticks)
# Turn off the axis
plt.axis(plot_axis)
# Display the figure
plt.show()
Display the mesh image
display_image(mesh_image_path)
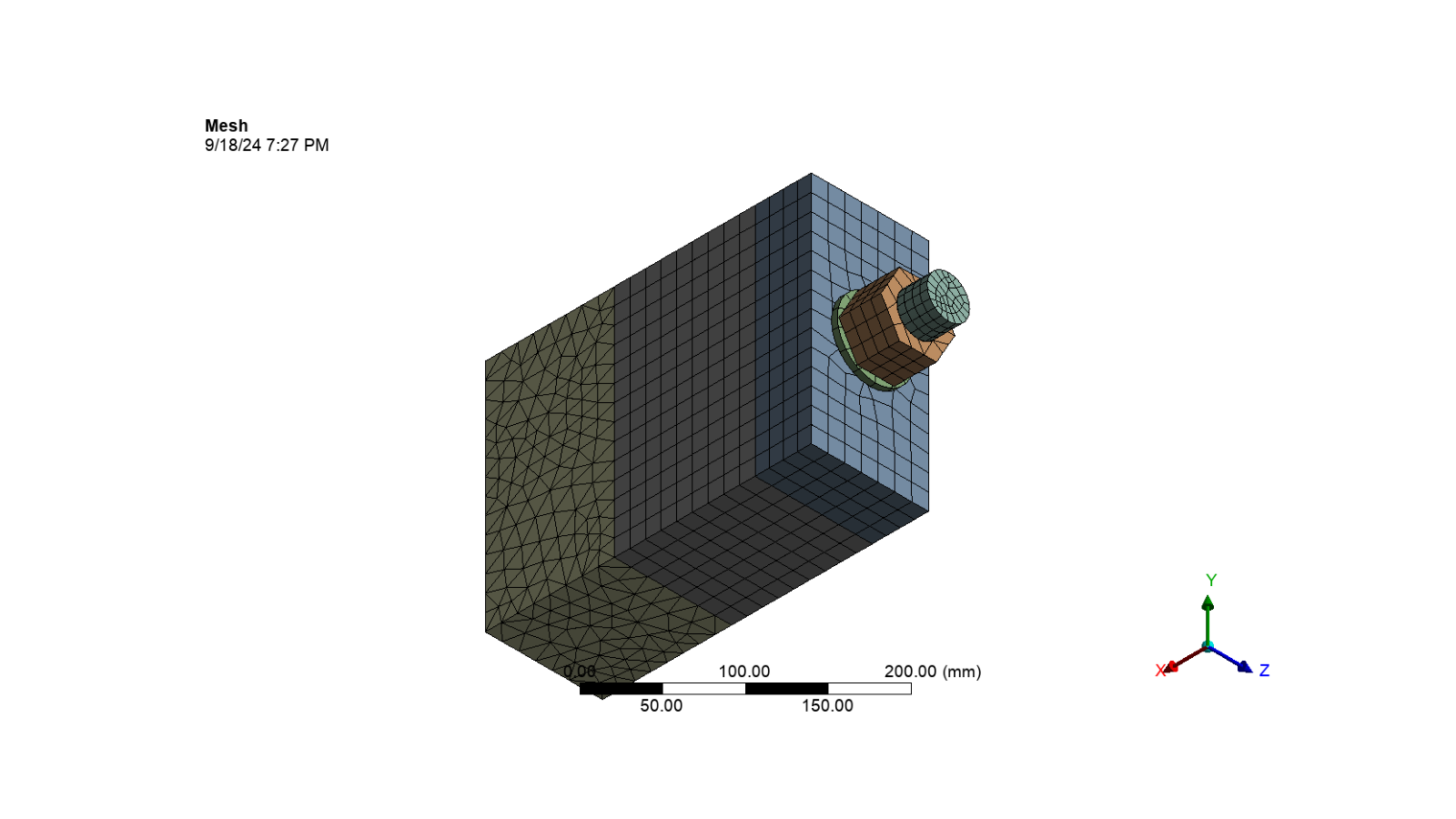
Analysis settings#
# Set the number of steps for the static structural analysis
static_structural_analysis_setting.NumberOfSteps = 4
# Set the step index list
step_index_list = [1]
# Set the automatic time stepping method for the static structural analysis
# based on the step index
with Transaction():
for step_index in step_index_list:
static_structural_analysis_setting.SetAutomaticTimeStepping(
step_index, AutomaticTimeStepping.Off
)
# Set the number of substeps for the static structural analysis
# based on the step index
with Transaction():
for step_index in step_index_list:
static_structural_analysis_setting.SetNumberOfSubSteps(step_index, 2)
# Activate the static structural analysis settings
static_structural_analysis_setting.Activate()
# Set the solver type and solver pivoting check for the static structural analysis
static_structural_analysis_setting.SolverType = SolverType.Direct
static_structural_analysis_setting.SolverPivotChecking = SolverPivotChecking.Off
Define loads and boundary conditions#
# Add fixed support to the static structural analysis
fixed_support = static_structural.AddFixedSupport()
# Set the fixed support location for the block2_surface object
set_mesh_method_location(method=fixed_support, object_name="block2_surface")
# Create a new force on the static structural analysis
tabular_force = static_structural.AddForce()
# Set the force location for the bottom_surface object
set_mesh_method_location(method=tabular_force, object_name="bottom_surface")
# Define the tabular force input and output components
tabular_force.DefineBy = LoadDefineBy.Components
tabular_force.XComponent.Inputs[0].DiscreteValues = [
Quantity(0, "s"),
Quantity(1, "s"),
Quantity(2, "s"),
Quantity(3, "s"),
Quantity(4, "s"),
]
tabular_force.XComponent.Output.DiscreteValues = [
Quantity(0, "N"),
Quantity(0, "N"),
Quantity(5.0e005, "N"),
Quantity(0, "N"),
Quantity(-5.0e005, "N"),
]
# Add a bolt presentation to the static structural analysis
bolt_presentation = static_structural.AddBoltPretension()
# Set the bolt presentation location for the shank_surface object
set_mesh_method_location(bolt_presentation, "shank_surface")
# Define the bolt presentation input and output components
bolt_presentation.Preload.Inputs[0].DiscreteValues = [
Quantity(1, "s"),
Quantity(2, "s"),
Quantity(3, "s"),
Quantity(4, "s"),
]
bolt_presentation.Preload.Output.DiscreteValues = [
Quantity(6.1363e005, "N"),
Quantity(0, "N"),
Quantity(0, "N"),
Quantity(0, "N"),
]
bolt_presentation.SetDefineBy(2, BoltLoadDefineBy.Lock)
bolt_presentation.SetDefineBy(3, BoltLoadDefineBy.Lock)
bolt_presentation.SetDefineBy(4, BoltLoadDefineBy.Lock)
# Activate the bolt presentation
app.Tree.Activate([bolt_presentation])
# Set the image path for the loads and boundary conditions
loads_boundary_conditions_image_path = str(
output_path / "loads_boundary_conditions.png"
)
# Export the image of the loads and boundary conditions
graphics.ExportImage(
loads_boundary_conditions_image_path,
image_export_format,
graphics_image_export_settings,
)
# Display the image of the loads and boundary conditions
display_image(loads_boundary_conditions_image_path)
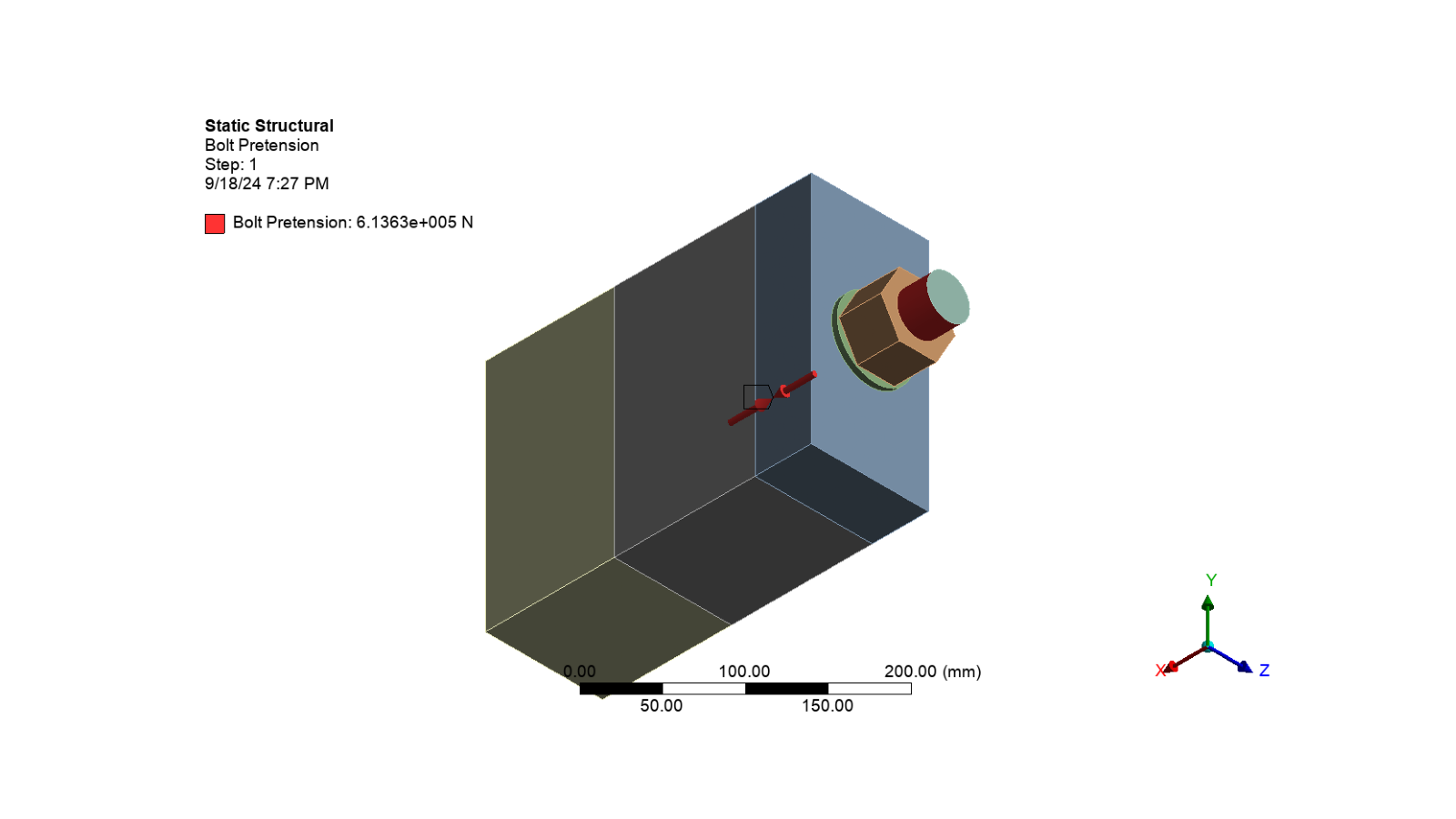
Insert results#
# Add a contact tool to the static structural solution and set the scoping method for it
post_contact_tool = static_structural_solution.AddContactTool()
post_contact_tool.ScopingMethod = GeometryDefineByType.Worksheet
# Add a bolt tool to the static structural solution and add a working load to it
bolt_tool = static_structural_solution.AddBoltTool()
bolt_tool.AddWorkingLoad()
# Add the total deformation to the static structural solution
total_deformation = static_structural_solution.AddTotalDeformation()
# Add equivalent stress to the static structural solution
equivalent_stress_1 = static_structural_solution.AddEquivalentStress()
# Add equivalent stress to the static structural solution and set the location for the shank object
equivalent_stress_2 = static_structural_solution.AddEquivalentStress()
set_mesh_method_location(method=equivalent_stress_2, object_name="shank")
# Add a force reaction to the static structural solution and set the boundary condition selection
# to the fixed support
force_reaction_1 = static_structural_solution.AddForceReaction()
force_reaction_1.BoundaryConditionSelection = fixed_support
# Add a moment reaction to the static structural solution and set the boundary condition selection
# to the fixed support
moment_reaction_2 = static_structural_solution.AddMomentReaction()
moment_reaction_2.BoundaryConditionSelection = fixed_support
Solve the static structural solution#
# Solve the static structural solution and wait for it to finish
static_structural_solution.Solve(True)
Show messages#
# Print all messages from Mechanical
app.messages.show()
Severity: Info
DisplayString: All contact results of contacts with MPC formulation are zero since constraint equations are used to bond the mesh together. Review results of the parts underlying the contact surfaces for more information.
Severity: Warning
DisplayString: One or more MPC or Lagrange Multiplier formulation based contact regions or remote boundary conditions may have conflicts with other applied boundary conditions or other contact or symmetry regions. This may reduce solution accuracy. For MPC based remote points, setting the relaxation method may help eliminate overconstraint. Tip: You may graphically display FE Connections from the Solution Information Object for non-cyclic analysis. Refer to Troubleshooting in the Help System for more details.
Severity: Warning
DisplayString: At least one body has been found to have only 1 element in at least 2 directions along with reduced integration. This situation can lead to invalid results or solver pivot errors. Consider changing to full integration element control or meshing with more elements. Offending bodies can be identified by Right-clicking in the Geometry window and choose Go To -> Bodies With One Element Through the Thickness. Refer to Troubleshooting in the Help System for more details.
Severity: Info
DisplayString: The requested license was received from the License Manager after 22 seconds.
Display the results#
Total deformation
# Activate the object
app.Tree.Activate([total_deformation])
# Set the camera to fit the model
camera.SetFit()
# Set the image name and path for the object
image_path = str(output_path / f"total_deformation.png")
# Export the image of the object
app.Graphics.ExportImage(
image_path, image_export_format, graphics_image_export_settings
)
# Display the image of the object
display_image(image_path)
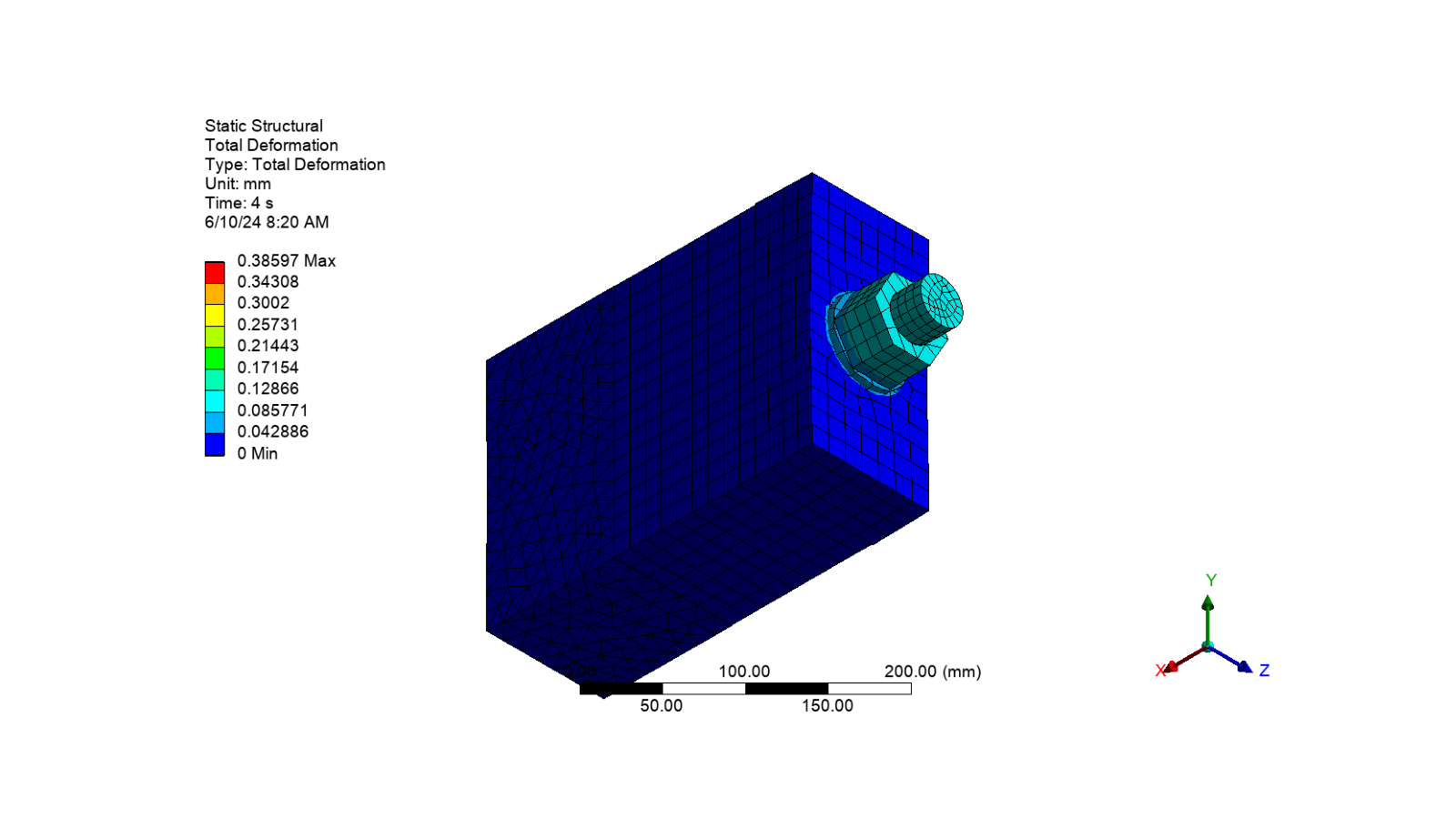
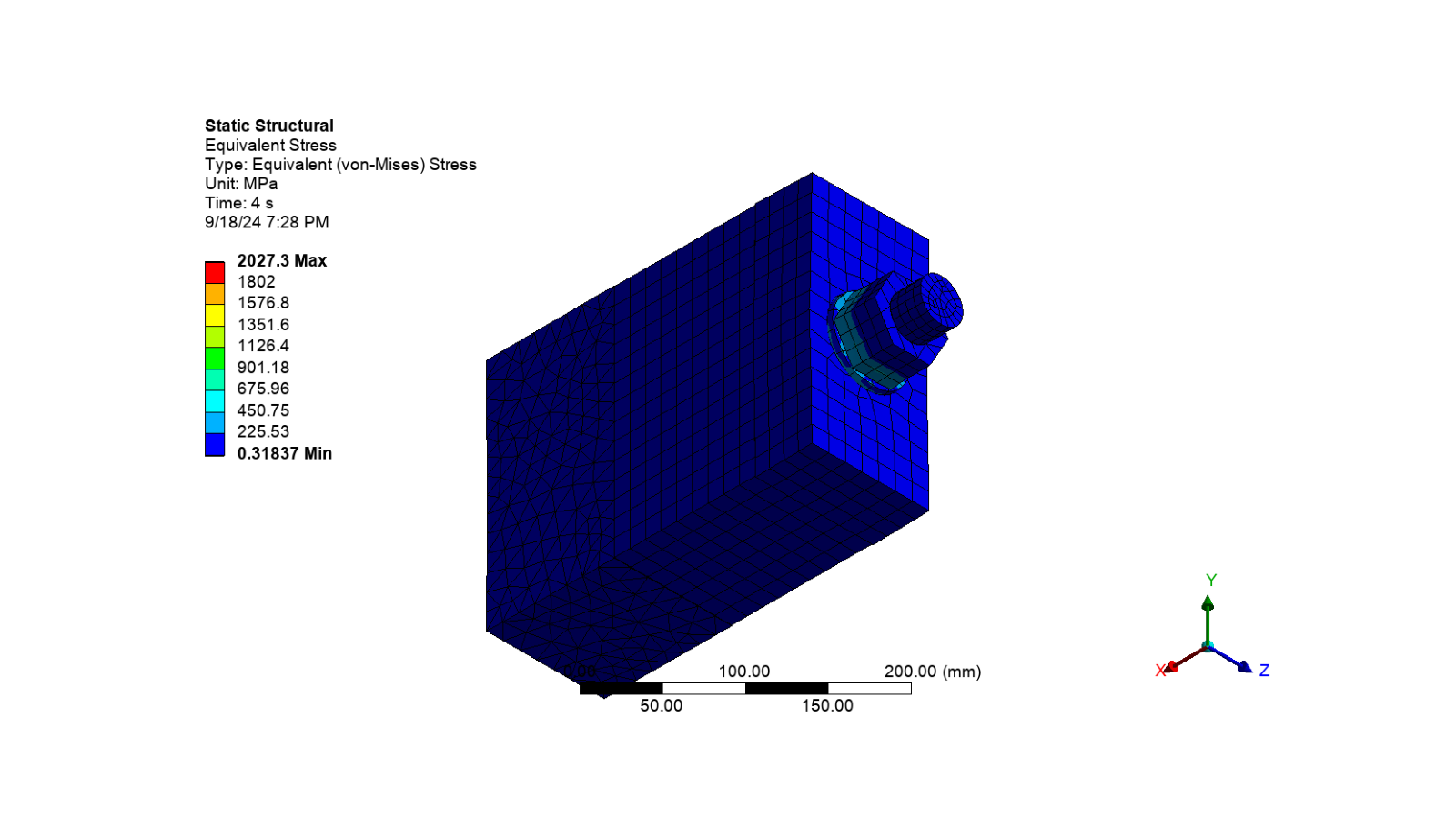
Equivalent stress on all bodies
# Activate the object
app.Tree.Activate([equivalent_stress_1])
# Set the camera to fit the model
camera.SetFit()
# Set the image name and path for the object
image_path = str(output_path / f"equivalent_stress_all_bodies.png")
# Export the image of the object
app.Graphics.ExportImage(
image_path, image_export_format, graphics_image_export_settings
)
# Display the image of the object
display_image(image_path)
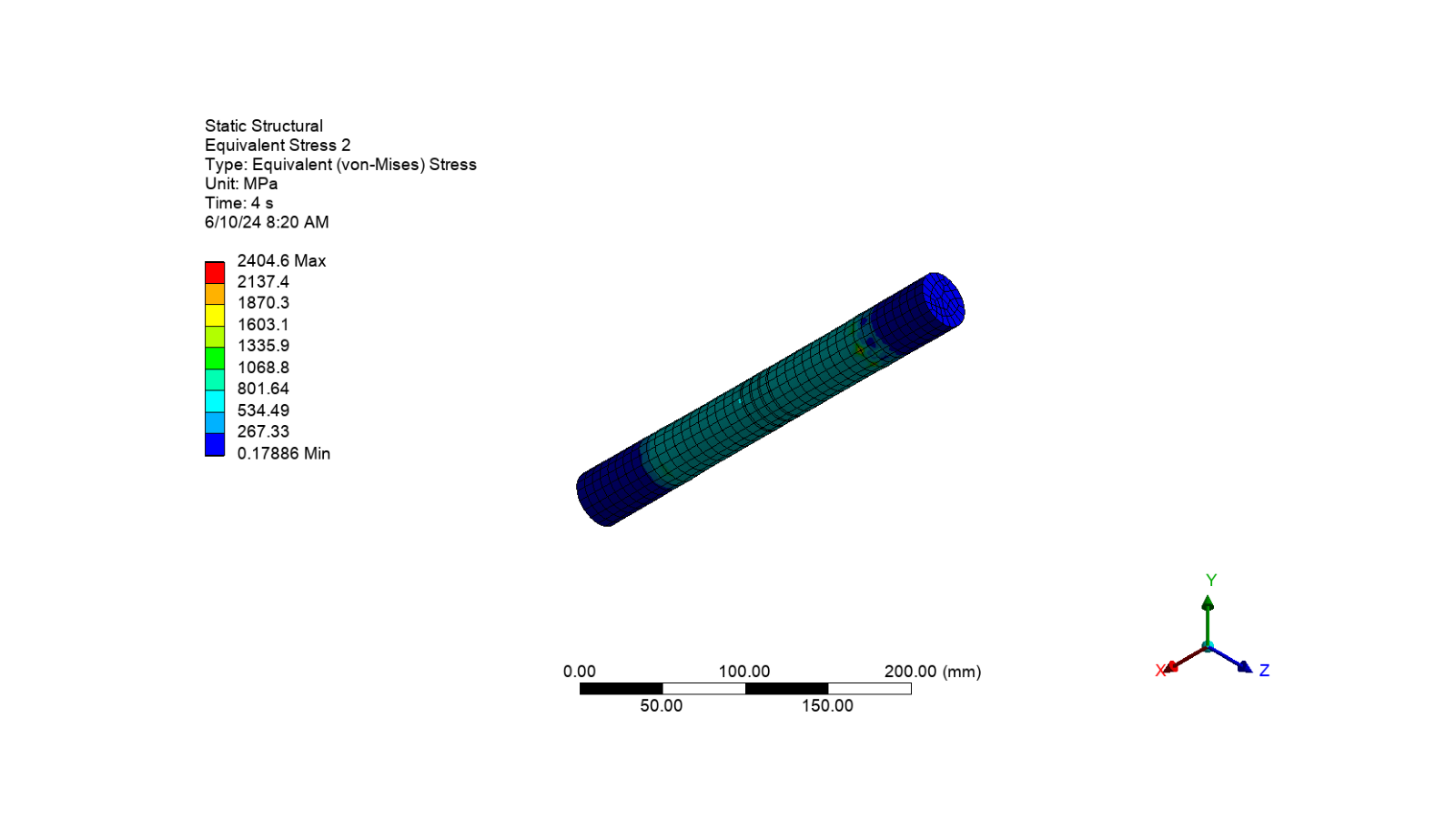
Equivalent stress on the shank
# Activate the object
app.Tree.Activate([equivalent_stress_2])
# Set the camera to fit the model
camera.SetFit()
# Set the image name and path for the object
image_path = str(output_path / f"equivalent_stress_shank.png")
# Export the image of the object
app.Graphics.ExportImage(
image_path, image_export_format, graphics_image_export_settings
)
# Display the image of the object
display_image(image_path)
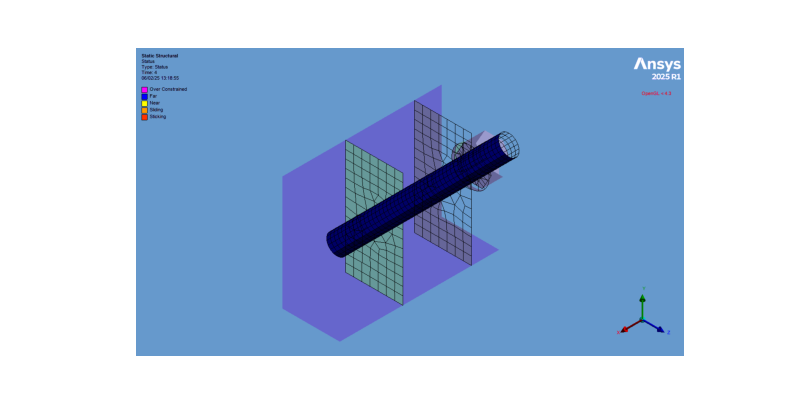
Export and display the contact status animation#
Create a function to update the animation frames
def update_animation(frame: int) -> list[mpimg.AxesImage]:
"""Update the animation frame for the GIF.
Parameters
----------
frame : int
The frame number to update the animation.
Returns
-------
list[mpimg.AxesImage]
A list containing the updated image for the animation.
"""
# Seeks to the given frame in this sequence file
gif.seek(frame)
# Set the image array to the current frame of the GIF
image.set_data(gif.convert("RGBA"))
# Return the updated image
return [image]
Export and display the contact status animation
# Get the post contact tool status
post_contact_tool_status = post_contact_tool.Children[0]
# Activate the post contact tool status in the tree
app.Tree.Activate([post_contact_tool_status])
# Set the camera to fit the model
camera.SetFit()
# Set the animation export format and settings
animation_export_format = GraphicsAnimationExportFormat.GIF
animation_export_settings = Ansys.Mechanical.Graphics.AnimationExportSettings()
animation_export_settings.Width = 1280
animation_export_settings.Height = 720
# Set the path for the contact status GIF
contact_status_gif_path = str(output_path / "contact_status.gif")
# Export the contact status animation to a GIF file
post_contact_tool_status.ExportAnimation(
contact_status_gif_path, animation_export_format, animation_export_settings
)
# Open the GIF file and create an animation
gif = Image.open(contact_status_gif_path)
# Set the subplots for the animation and turn off the axis
figure, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4))
axes.axis("off")
# Change the color of the image
image = axes.imshow(gif.convert("RGBA"))
# Create the animation using the figure, update_animation function, and the GIF frames
# Set the interval between frames to 200 milliseconds and repeat the animation
FuncAnimation(
figure,
update_animation,
frames=range(gif.n_frames),
interval=200,
repeat=True,
blit=True,
)
# Show the animation
plt.show()
Print the project tree#
app.print_tree()
├── Project
| ├── Model
| | ├── Geometry Imports (✓)
| | | ├── Geometry Import (✓)
| | ├── Geometry (✓)
| | | ├── Solid
| | | | ├── Solid
| | | ├── Solid
| | | | ├── Solid
| | | ├── Solid
| | | | ├── Solid
| | | ├── Solid
| | | | ├── Solid
| | | ├── Solid
| | | | ├── Solid
| | | ├── Solid
| | | | ├── Solid
| | ├── Materials (✓)
| | | ├── Structural Steel (✓)
| | | ├── Copper (✓)
| | | ├── Steel (✓)
| | ├── Coordinate Systems (✓)
| | | ├── Global Coordinate System (✓)
| | | ├── Coordinate System (✓)
| | ├── Remote Points (✓)
| | ├── Connections (✓)
| | | ├── Connection Group (✓)
| | | | ├── Contact Region (✓)
| | | | | ├── Commands (APDL) (✓)
| | | | ├── Contact Region 2 (✓)
| | | | ├── Contact Region 3 (✓)
| | | | | ├── Commands (APDL) (✓)
| | | | ├── Contact Region 4 (✓)
| | | | ├── Contact Region 5 (✓)
| | | | ├── Contact Region 6 (✓)
| | | | | ├── Commands (APDL) (✓)
| | ├── Mesh (✓)
| | | ├── Body Sizing (✓)
| | | ├── Body Sizing 2 (✓)
| | | ├── Automatic Method (✓)
| | | ├── Face Meshing (✓)
| | | ├── Method (✓)
| | ├── Named Selections
| | | ├── block3_block2_cont (✓)
| | | ├── block3_block2_targ (✓)
| | | ├── shank_block3_targ (✓)
| | | ├── shank_block3_cont (✓)
| | | ├── block1_washer_cont (✓)
| | | ├── block1_washer_targ (✓)
| | | ├── washer_bolt_cont (✓)
| | | ├── washer_bolt_targ (✓)
| | | ├── shank_bolt_targ (✓)
| | | ├── shank_bolt_cont (✓)
| | | ├── block2_block1_cont (✓)
| | | ├── block2_block1_targ (✓)
| | | ├── all_bodies (✓)
| | | ├── bodies_5 (✓)
| | | ├── shank (✓)
| | | ├── shank_face (✓)
| | | ├── shank_face2 (✓)
| | | ├── bottom_surface (✓)
| | | ├── block2_surface (✓)
| | | ├── shank_surface (✓)
| | ├── Static Structural (✓)
| | | ├── Analysis Settings (✓)
| | | ├── Fixed Support (✓)
| | | ├── Force (✓)
| | | ├── Bolt Pretension (✓)
| | | ├── Solution (✓)
| | | | ├── Solution Information (✓)
| | | | ├── Total Deformation (✓)
| | | | ├── Equivalent Stress (✓)
| | | | ├── Equivalent Stress 2 (✓)
| | | | ├── Contact Tool (✓)
| | | | | ├── Status (✓)
| | | | ├── Force Reaction (✓)
| | | | ├── Moment Reaction (✓)
| | | | ├── Bolt Tool (✓)
| | | | | ├── Adjustment (✓)
| | | | | ├── Working Load (✓)
... truncating after 80 lines
Clean up the project#
# Save the project
bolt_presentation_mechdat_path = str(output_path / "bolt_pretension.mechdat")
app.save(bolt_presentation_mechdat_path)
# Close the app
app.close()
# Delete the example files
delete_downloads()
True
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 10.828 seconds)

